From time to time I am asked about what methods of connecting to the Internet exist and what type of access to the global network is best to choose for a country house or a house located within the city. But indeed, the IT market has literally become overgrown with companies that provide Internet access services. What technologies are not used today in wireless and wired connections in order to maximally cover hard-to-reach areas, increase data transfer speeds, improve communication quality...
As you know, Internet providers differ in the provision of services, namely the type of access to the Internet.
Internet provider - a company that provides Internet access to its client and provides other related services.
There are such types of Internet connections as broadband, dial-up and wireless communication lines. All of them are capable of opening up the world of the Internet to you, although they work on different principles. But first things first.
Ethernet - connection via local network.
This is a fixed broadband Internet access via a dedicated line. The line provided by the provider is built on fiber optic or copper cable, which makes it possible to transfer data to computers at high speed. The material used to create a fiber optic cable is glass or plastic, and information is transmitted through it not by an electrical signal, but by a light signal, which allows the signal to be transmitted over vast distances with negligible attenuation.
Copper cable means a twisted pair (described here) through which information is transmitted by an electrical signal. Due to its peculiarity, twisted pair, unlike fiber optic cable, has a significant signal attenuation rate and is susceptible to electromagnetic interference. To increase the length of the communication channel, you should use cables that are protected from interference and interference, and to reduce the signal attenuation coefficient, you need to use special correctors or signal buffers.
However, do Internet providers do this in practice where it is needed? It should be said that usually a fiber optic cable is used to connect a subprovider with a backbone provider and connect various buildings (multi-storey buildings, hotels...) to the global network, and then there is a twisted pair cable.
True, GPON (gigabit passive optical network) technology is now actively developing. Its essence lies in the fact that the provider runs a fiber-optic cable directly to your apartment and installs a special separation box. In this situation, you technically have the opportunity to connect to the global network at a speed of 1 Gbit/s, but in other cases the speed will not exceed 100 Mbit/s.
Be that as it may, a leased line is most optimally suited for connecting to the Internet at home (read more about that) or obtaining shared access to the network in the office. As a rule, providers with this type of connection offer unlimited Internet, which means you will not need to worry about wasting network traffic downloading information or surfing the Internet. Using a Wi-Fi router, you can connect other digital devices (smartphone, tablet, laptop, Smart TV...) to the Internet.
The high speed of the Internet channel in Ethernet technology makes it possible to quickly download impressive amounts of information, comfortably work on the network with multimedia and conduct various video meetings online. Many providers that provide Internet access via a dedicated line offer IP television (IPTV) as an additional service, where some channels can be presented in HD format. This is perhaps one of the best ways to connect to the Internet.
Modem connection (ADSL and Dial-Up).
This is dial-up access to the Internet via a telephone line using a modem. You can connect to the Internet via a telephone line using the old Dial-Up technology or the more advanced ADSL technology. Connecting to a provider using ADSL, unlike Dial-UP, makes it possible to surf the Internet and simultaneously make phone calls. This is achieved through an ADSL splitter, which divides the telephone signal into a regular telephone signal and a high-frequency modem signal.
Compared to a dedicated line connection (the method described above), the advantage of a modem connection is that existing telephone cables are used, but this is where the advantage of this Internet access ends. The maximum data transfer speed for Dial-Up is 56 Kbps, and for ADSL technology 24 Mbps, but given the state of the telephone lines, connection stability may not have such indicators.
![]()
![]()
As you understand, a telephone line is inferior to a leased line in all respects, taking into account the stable growth of multimedia and the volume of transmitted data. Just a few years ago, this type of connection was considered one of the best, but these days it has practically become obsolete, despite the fact that it is still used as an alternative connection to the Internet where, for some reason, using another connection is not relevant.
Internet connection using DOCSIS technology.
Literally, DOCSIS (Data Over Cable Service Interface Specifications) is translated as a standard for data transmission over a coaxial (television) cable. Data transmission according to this standard from the provider is carried out to the client (downstream) at a speed of 42/38 Mbit/s, and from the user (upstream) 10/9 Mbit/s. It is worth saying that the bandwidth in this technology is divided between all connected participants who are currently receiving or sending information flow. Consequently, the available bandwidth at the time of data transmission or reception for each user can vary within wide limits.
This method of connecting to the Internet, like the previous one, is performed through a special modem. This is a cable modem for DOCSIS technology with a built-in network bridge, which makes it possible to exchange data over a coaxial or optical cable in two-way mode. It should be noted that in the network of such a provider there is a CMTS device - Cable Modem Termination System. In short and simply, this device is a large modem in the backbone network to which subscriber modems are connected.
![]()
![]()
From an economic point of view, laying a coaxial cable in order to gain access to the Internet is not very reasonable; it is better to install a dedicated line (ethernet connection), because such a line is better in terms of technical characteristics, but if there is already a television cable in the house and your cable TV operator provides one service, then why not use it. However, if your provider can provide you with Internet access using FTTB, PON or HCNA technology, then for a number of technical advantages it is better to choose one of them instead of traditional DOCSIS.
Mobile Internet access (GPRS, EDGE, 3G).
This type of Internet connection is popular because it makes it possible to access the Internet in areas where there is no telephone or leased line. You can connect to an Internet provider using a USB 3G modem or using a mobile phone (iPhone, smartphone, communicator) with a modem function. A USB modem is visually similar to a USB flash drive and has a slot inside for installing a SIM card.
Connecting to the Internet, via a USB modem or mobile phone, is carried out by “accessing” the base station of the cellular operator with whom you are served, and depending on what equipment is installed at the mobile provider, communication is established using GPRS, EDGE, 3G or HSDPA (4G). Thus, after connecting a USB modem or phone (via a USB cable, infrared port or Blurtooth) to a computer, you will gain access to the Internet using one of the mentioned technologies.
![]()
![]()
Mobile Internet has unstable connection quality and rather low speed, but it is quite suitable for loading pages normally into the browser. The maximum data transfer speed in the presented technologies is on average 20-40 Kbps in GPRS; 100-236 Kbps in EDGE; 144 Kbps - 3.6 Mbps in 3G and 4G can exceed 100 Mbps, and for landline subscribers it can be 1 Gbps.
Speed characteristics, depending on the technologies used by the Internet provider, in some cases may be higher, but in almost all cases they are lower. Mobile Internet, of course, has many disadvantages, but being able to access the global network from anywhere in the country captivates many of us.
Now let's look at the wireless Internet connection (satellite, WiMAX). These types of wireless Internet connections are good because they can be used where it is not yet possible to access the network via cable for some reason.
Using wireless technologies, you can access the Internet outside the city, where wired Internet is not available. For example, in a country house, warehouse, office or some other facility. It must be said that such methods of connecting to the Internet require the presence of additional equipment, and its purchase in some cases can cost you a tidy sum.
Internet via satellite dish.
For example, to connect one-way satellite Internet you will need a small set of equipment. You need to buy a satellite antenna, a converter amplifier (selected for the C, Ka or Ku band and linear or circular polarization of the operator), a satellite receiver (PCI card or USB receiver), a cable of the required length, type RG-6 (75 Ohm) and a pair F-connectors.
For two-way access to satellite Internet, you need a transceiver antenna (about 1.2 - 1.8 meters in diameter), a transmitting BUC (block-up converter) and a receiving LNB (low-noise block) block and a satellite modem to which you can connect more than one , and several computers and provide them with Internet access. Use the range recommended by the satellite operator.
![]()
![]()
Each of these satellite Internet connections has its own characteristics. For one-way access, you need already existing Internet access (for example, GPRS or EDGE), through which the sent requests will be processed by the Internet provider (one-way access), and after processing the received data will be sent to its client via the satellite corridor.
![]()
![]()
With two-way Internet access, no additional channels are needed, since data is sent and received via satellite. Many satellite Internet operators can offer both unlimited packages and a pay-per-traffic tariff. Two-way satellite Internet for some operators is faster than 3G technology, and the speed in the Ka-band can be 20 Mbit/s.
The disadvantages of this technology can be considered the high cost of equipment, the difficulty of setting up equipment for a technically inexperienced user, and the long response time (delay). Usually they use satellite Internet in remote corners of the country, where there is no other acceptable alternative. Using a Wi-Fi router with a satellite connection to a provider, as well as in other technologies, will give you the opportunity to distribute the Internet via wireless communication and LAN cable to other digital devices (laptop, tablet) in the house.
We have already looked at different methods of connecting to the Internet, including mobile access, but I would like to draw your attention to another type of Internet connection using WiMax technology. Often, this Internet access technology is used where cable Internet of the DOCSIS standard is not available, there is no dedicated network in the home or office, or there is no telephone line for an ADSL connection. Access to the global network via WiMax technology, as well as via satellite connection, often plays a decisive role in such cases.
WiMax technology theoretically has a data transfer speed of about 70 Mbit/s, but in practice this speed is several times lower. To connect to the Internet using WiMax technology, you need to contact the providing provider, who will determine from the network coverage map whether your location is within the coverage area. If it turns out that your location does not fall within the coverage area, then specialists will need to determine the distance to the nearest base station to you.
It is desirable that the base station be in direct line of sight (not necessary) from you, and the distance should be no more than 10 kilometers. Depending on the results obtained (distance and signal reception conditions), you will need to select a WiMax modem and antenna with the required gain. In addition, you will need a cable to connect the antenna to the modem and a USB extension cable to connect the modem to a router or computer.
![]()
![]()
The antenna is usually installed at the highest possible point and directed (Google Earth can be used for calculation) as accurately as possible to the base station. After this, the antenna is connected to the modem, connected to the network and adjusted to the maximum signal level. Very often, to receive the Internet via WiMax, they use a specialized Wi-Fi router with a USB port that can work as a WiMax modem.
Thus, via a wireless Wi-Fi network (read if) you can open Internet access to other digital devices (tablet, laptop...). Both Wi-Fi and WiMax technologies are wireless and are used to gain access to the Internet, but despite this they solve a different range of problems. As a rule, Wi-Fi is used to build wireless local networks with a range of 50 to 100 meters depending on the environment.
Unlike WiMax, Wi-Fi technology is little used by Internet providers, but this type of wireless Internet connection has gained great popularity in hotels, airports, cafes, clubs, apartments and houses. Because this technology allows you to quickly, easily and conveniently provide everyone who wants to access the global network with wireless Internet. Look at the comparison table of these standards and read.
Now in general terms you know what methods of connecting to the Internet exist. Of course, information technology does not stand still, but is rapidly developing in our world and the speed of data transfer is constantly increasing.
2018-09-05T13:52:24+00:00
Guys, this is bullshit. I bought 1000 Mbit/sec Internet, what happens if I connect it to a router that only provides 100 Mbit/sec?
2018-08-15T17:46:57+00:00
Folks, is it possible to combine traffic from the network and mobile Internet like a thread on a regular PC? The Internet is slow at work, but the phone lags. At the same time, how can this be compacted into one channel?
2018-06-20T23:07:08+00:00
This article really needs updating, but I don’t have time for that yet. If we manage to assemble a team, then all the articles will be rewritten or supplemented. In the meantime, everyone is free to add to it in the comments, however, there are not many of them, but there are many times more criticizing. But this is good, because I point out mistakes, which means there is room for improvement.
2018-06-16T16:07:22+00:00
Dmitry, what the hell satellite antenna do you mean? It’s a hundred times cheaper to do a cable transfer. And Kizeev meant Kharchenko’s antennas or a wave channel (Yaga). Do you agree? And thank you for the article. But about the leased line (Ethernet) in more detail: it’s a little expensive and there’s a stat. IP address?
2017-12-15T15:51:45+00:00
Hello Dmitry. I read a lot of reviews, but only yours interested me. Since I am a single pensioner, I only need one regular Internet connection cable without a router, but everywhere there is only a router and a fiberglass cable, and this, accordingly, is the price. Now I have Beeline, but there are some tricks all the time - I only pay 450 rubles. but you need 900 rubles. And so I’m struggling with my pension: paying for my mobile phone, paying for electricity and housing and communal services. So I'm guessing. And we, pensioners, also want to live, of course, not like everyone else, but we try “not to lose face.” Sorry. Perhaps you have your own business, and you have no time for us. Sincerely, Ludmila
The Internet has long become the norm for all inhabitants of the planet. Thanks to it, money transactions are carried out, people watch TV shows, study at master classes, and learn previously unknown information. However, connecting to the Internet is not so easy. You must be connected via a local network, through a mobile provider, or some other means. Connection to the Internet is carried out using fiber optic cable, twisted pair, ADSL, or wireless Wi-Fi.
Cable connection
The most common type of connection is cable. This type of connection is made using twisted pair or optical fiber. twisted pair is a cable consisting of four pairs of copper wires. It receives and transmits signals. Modern providers provide Internet to apartment buildings in this manner: a router is installed, a wire comes to it and, using a connector, is connected to a distributor, from which wires are already distributed to apartments. At the point of connection with the computer, the ends of these wires are crimped with a connector.
twisted pair
Optical fiber is already a more modern means of transmitting information at a distance. It is also connected and has almost the same distribution boxes as twisted pair, but with the difference that the optical cable information is transmitted with speeds up to 1 GB per second, while over twisted pair cable only up to 100 MB/sec.
 Fiber optic connection
Fiber optic connection Connecting FTTB or fiber to the home is a connection to the World Wide Web using optical fiber, and distribution throughout the apartment is using twisted pair.
Twisted pair is connected or directly to the system unit, or to home wifi router Using this connection, it is possible to provide users’ apartments not only with the Internet, but also with telephone and digital television.
GPon is gigabit communication channel. It provides users with high-speed access up to 1 gigabit per second. The cable is connected in the user’s apartment to a special media converter, which in turn receives data and distributes it to the user’s devices. Such equipment began to appear in our megacities quite recently.
The local network
The principle of local connection is to connect several computers at home or in a factory into one network, for which the provider allocates an IP address. Such an address can be static or dynamic.
When connecting using dynamicIP, the provider constantly automatically assigns you the necessary settings at certain intervals. Nothing is required from you, just plug the cable into your computer and connect to the Internet.
StaticIP differs from the first in that the provider provides the settings to the user and he himself configures his computers, network card and Internet access. The positive side of a static IP is that it is convenient for working with online services that ask you for an IP address. The router most often automatically detects the IP.
This technology is called Ethernet.
VPN network
A virtual private network or VPN is a technology for encrypting data. This way your data is protected during transmission. They reach the provider safely and securely. Working with a virtual private network is most often implemented in several ways:

Combined connection
This type of connection combines several types of connections simultaneously. Typically the first is a virtual private network, and the second is a dynamic or static IP. This connection is rarely used, as it is the most complex.
Phone line
Nowadays, cable connections predominate in the world, and the telephone line is gradually becoming a thing of the past. But in areas so far from large cities or desert areas, it still has its significance, because it is not practical and expensive to run the cable there.
Internet via home phone is transmitted over the telephone line several types of communication:
- ADSL, SHDSL, VDSL are types of digital subscriber line or DSL. ADSL uses a telephone line to transmit data and is connected to a computer via a modem and cables. In addition, using this connection, not only the Internet, but also the telephone works. Is it true, throughput this type of connection is very small compared to modern cable installations. If the first one uses asymmetrical data transmission, then SHDSL, in turn, uses symmetrical duplex transmission. The speed of such a connection on one pair is no more than 2.3 Megabits per second. VDSL is super high speed digital subscriber line. This technology is used when connecting optical fiber from the provider to the user switch, and from the latter via twisted pair cable to the system unit. Using this technology, high data reception speeds are achieved over short periods.
- DIAL UP (dial-up) is the oldest type of data transmission over a telephone line. Transmission speed about 56 kilobits per second. You cannot make phone calls at this time, otherwise your connection to the Internet will be lost. The modem is connected to the telephone line and to the computer. The modem connects by number, and the user gains access to the network.
TV cable DOCSIS
Access is via TV cable. It is brought into the apartment with a subscription and distributed to the TV and modem or goes straight to the computer. 300 megabits per second is his maximum speed. But this type of connection is not common.
This type of data transmission has become the most popular recently. After all, no cables or routers are needed. Most importantly, you must have a phone with you that supports 2G, 3G, 4G and is within the coverage area of your telecom provider.
2G – the slowest telephone connection technology. Used before on the first smartphones. Its speed is measured in kilobits per second. Also called GPRS, which replaced the GSM standard
3G (3rd Generation) - this connection model is also becoming obsolete, but still in use. Its speed reaches 40 megabits per second.
4G/LTE is a new network connection format that supports speed data transfer up to 300 megabits per second.
5G is replacing all standards. This type of connection is still being tested. But they are committed to introducing it in Western countries by 2020. He has already passed the first test quite successfully. In Russia, the first tests of 5G technology will be carried out during the FIFA World Cup, which will be held in 2018. 
Satellite Internet
Satellite Internet is the most expensive. There are two types of such network entry - one-way and two-way. At unilaterally transmission occurs over a terrestrial channel, and when bilateral the exchange takes place via satellite. The speed reaches tens of megabits per second.
WiMax or Wi-Fi
WiMax is a connection using highly targeted microwaves. This type of network access is used on long distances and provides broadband connectivity, and it also uses the MAC Address Protocol.
Wi-Fi is needed for broadband Internet access within the office or at home. It operates on unlicensed bands. This type of communication is more common and adapted for the average user.
FAQ
Now we understand how communication with the World Wide Web occurs through our devices. But many users ask questions about what is broadband, open internet or others. Therefore, let's look at the most common of them.
Open Internet is often used by providers in the names of tariffs. This is the Internet which is charged after the end of the traffic, which is included in the subscription fee.
Broadband access (broadband) is access to the network at a speed much larger than the speed of the modem or telephone network.
Some people are interested in what types of networks there are. There are three connection types:
- LAN– local computer networks. These networks belong mainly to one organization and have a coverage of several kilometers or tens of meters. Such networks can be connected to each other through a ring. Or in linear mode using routers. The second method is much more convenient and effective.
- Regional networks. Their coverage reaches 100 kilometers. Usually these are city and regional networks.
- Global. Essentially, this is the Internet network, which connects all the computers in the world into one big web.
In addition, you can highlight division by communication method (wired and wireless), control method (with centralized and decentralized control) and by the composition of computing tools (homogeneous and heterogeneous).
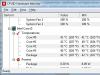
And finally, if you want to find out the type of connection your computer has to the Internet, to do this you need to right-click on the computer icon in the lower right corner of the screen and open network control center and general access. 
In the window that opens, click " Change adapter settings». 
You will see a window on the screen where all your connections will be displayed. 
The one without the red cross icon is the current connection. To find out in more detail, it is better to contact your provider, or determine the type based on the above methods.
Almost every owner of a personal computer, almost immediately after purchasing it, thinks about the issue of connecting to the World Wide Web, which makes it possible to communicate with people from all over the world, download and search for the necessary information, use all kinds of services (email, streaming multimedia) and services (web forums, blogs, online stores), and much more. Of course, the user is faced with the question: how to connect to the global network and what methods of this connection exist? If just a few years ago the majority of network users in the Russian Federation essentially had no choice but to use a modem connection via a telephone line (Dial-Up connection), now the situation in the information services market has changed significantly. This material is designed to help you understand among the multiple options for connecting to the network and choose the most optimal one for you.
NETWORK CONNECTION METHODS
At the moment, the most common methods of connecting to the World Wide Web are:
- An ordinary modem connection or the so-called dial-up access
- Modem connection via asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL)
- Broadband access over a leased line (Ethernet)
- Access using Mobile WiMAX technology
- Access via Wi-Fi technology
- Mobile GPRS/3G access
- Satellite network connection
They differ in the principle of operation, the speed of sending data, reliability, the difficulty of setting up equipment, and, of course, cost.
CONNECTION SPEED
It is worth talking separately about the fundamental characteristic of each connection to the World Wide Web - the data transfer speed, which is determined by the amount transmitted to the user per unit of time (per 1 second). Typically, the amount of data transferred is determined either in kilobytes/second (KB/s) or kilobits/second (kbps). For ordinary users, the measurement in bytes is more understandable, since it does not contain cumbersome numbers. Remember that 1 byte = 8 bits, and this ratio remains true for quantities with prefixes: kilo, mega or giga. Knowing how to convert bytes to bits will come in handy when you start studying the tariffs of Internet providers who really like to indicate the Internet connection speed in bits, since in this case the figure turns out to be more impressive (8 times). Also keep in mind that for channels with high connection speeds, the measurement is already in megabits or megabytes per second.
To make everything completely clear, let's look at a small real example. If the provider promises you a speed of 5 Mbit/s, which is equivalent to 0.625 MB/sec (divide 5 by 8), this means that at best you will download a 100 MB file from the network in less than three minutes (100 / 0.625 = 160 sec).
Each user's use of the Internet can be different; for some it involves receiving a large amount of Internet traffic, for others it does not. For example, for ordinary web surfing (viewing website pages), the speed of an ordinary modem connection is sufficient, but this speed will not allow you to comfortably download large files from the network - high-quality music or films, software distributions and other “heavy” content. To take full advantage of the Internet, you will need higher speed access.
So, having understood the connection methods and the concept of connection speed, let's move on to their description.
DIAL ACCESS (DIAL-UP)
This is the “oldest” and widely used method of connecting to the global network using a modem and telephone line. However, in our time, it is being actively replaced by more modern connection methods and is now used either in rural (remote) areas where there is no possibility of connecting to the network using high-speed lines or by users with a very limited budget.
With this connection method, the user, every time to enter the global network, will have to dial through a telephone line using a modem in order to “get” to the provider’s modem pool. Following this, the provider checks the user's login name and password. If the entered parameters are successfully processed, the subscriber is assigned a free IP address, through which he gains access to the Internet.
.jpg)

The advantages of such a connection are: ease of configuration and installation of equipment (only a modem is needed), low cost of equipment.
There are many more disadvantages to a modem connection. Busy telephone line at the moment when you are on the network, low speed of information transfer (usually 3-5 kb/s), low quality of communication and data transfer due to wear and tear of telephone lines and outdated equipment on the PBX. It is clear that with the speed provided by a modem connection, it is impossible to download large files from the Internet - videos, software distributions, etc.
To connect using this method, you will need an internal analog modem in case of a high-quality telephone line, or an external one if your telephone line leaves much to be desired.
HIGH SPEED ACCESS WITH ADSL TECHNOLOGY
A much more advanced and modern connection method compared to Dial-up connection. Literally, the abbreviation ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) can be translated as: “asymmetric digital subscriber line.” This technology allows you to provide high-speed access to the worldwide network via ordinary analog telephone wires (lines) using a special modem. Unfortunately, this connection method has one significant limitation - the PBX serving you must have ADSL equipment (multiplexer) installed. And if in large cities this is not a problem, then in the periphery many users may not have access to such a connection.

The main advantage of this method is the ease of installation and connection of equipment, as in the case of dial-up access (you only need a modem), and the maximum throughput of such a connection reaches 8 Mbit/s (up to 24 Mbit/s in the case of ADSL 2+). This is quite enough for effective work with various types of data and multimedia content. In addition, the technology does not load the regular telephone channel, and the subscriber does not need to dial up the provider, since the connection is permanent.
It must also be said about the possible disadvantages of this connection method. Not every user can be satisfied with the price of connection and the subscription fee charged by the provider for its services. And if in many European countries ADSL is the de facto standard for providing the population with inexpensive and fairly fast Internet, then in Russian conditions, a lot will depend on the region and the number of competing providers. In the absence of any competition in this area, you may be faced with greatly inflated rates.
There is one more negative point in ADSL technology, which is worth paying attention to all fans of peer-to-peer networks that use torrent clients to download information from the network. When using this type of connection, the speed of receiving (downloading) information from the Internet is much higher than uploading it, which violates the basic principles of file sharing in such networks.
Required equipment:
- ADSL modem
- ADSL splitter (usually included with the modem)
BROADBAND ACCESS
It is the optimal connection, as it can provide the highest speed of receiving and transmitting information on the global network (up to 100 Mbit/s). Broadband access makes it possible to use the Internet, its services and services with full efficiency and effectiveness.
In this case, the connection is made by the Internet provider, which runs a dedicated line (usually a twisted pair cable) to the subscriber’s computer (apartment) and issues a range of IP addresses for the subscriber to access the Internet.

The obvious advantages of this connection method are not only the high speed of information exchange, but also a free telephone number, constant interaction with the network, and excellent communication quality.
The only obstacle for many users may be the cost of installing and setting up such a connection, which directly depends on the distance of your computer to the connection point of the provider. Most likely, it will be higher compared to other connection methods. However, it is worth noting that: firstly, this is a one-time payment, and secondly, many providers, in order to attract customers, provide free connections.
To connect one computer, the user only needs a network card. Nowadays it is built into almost any computer. If you are deploying a home network for several computers that support a wireless connection, you will need an additional wireless router.
ACCESS THROUGH TECHNOLOGYMOBILEWIMAX
This technology is used to provide wireless broadband Internet access. WiMAX is a long-range system that covers kilometers of space and allows the user to receive both fixed access (similar to the usual xDSL only without wires) and mobile access, allowing you to connect to the network from anywhere within the coverage area. As a rule, fixed access is used to deploy small office and regional networks, but mobile access is aimed at the end user.
The first and largest mobile WiMAX network in Russia was deployed by Yota. The maximum data exchange speed in such networks is up to 10 Mbit/s, which allows you to comfortably download large files, watch videos or participate in on-line games. The connection to Yota itself is carried out using a special modem (usually in the form of a USB key fob) in a matter of minutes.

Unfortunately, the most important disadvantage of such a connection is its very limited distribution in the Russian Federation. At the moment, Mobile WiMAX from Yota is available only in eight cities of Russia (Moscow, St. Petersburg, Krasnodar, Sochi, Ufa, Vyborg, Luga and Serpukhov), and even within them in many areas the signal level leaves much to be desired.
ACCESS THROUGH TECHNOLOGYWI-FI
Unlike WiMAX, Wi-Fi is a system that covers much smaller spaces (no more than 150-200 m with one access point) and is usually used by users to access their own local networks, which, by the way, may not be connected to the Internet. This is an excellent solution for simultaneously connecting several computers to a network wirelessly, both at home and in a small office.
.jpg)
The access point itself, broadcasting the Wi-Fi radio signal, is connected to the World Wide Web using a wired connection. Wi-Fi networks are also often used in restaurants, cafes, shopping malls, airports and railway stations, through which visitors to these places can access the Internet for free. Thus, we can say that this technology is an auxiliary tool that allows many users to simultaneously use the capabilities of one broadband Internet connection point.
MOBILE INTERNET (GPRS/3G).
Due to the very rapid development of mobile communications in the Russian Federation, probably every adult already has a mobile phone. And if desired, it can also be used to access the global network. In fact, all providers these days offer the service of using a cell phone instead of a traditional modem, creating all sorts of special tariffs for this. In addition, almost all operators now offer independent solutions in the form of specialized GPRS/3G modems or routers with Wi-Fi support that can provide Internet access via mobile networks.
As a rule, this type of connection is the prerogative of users of mobile computers (laptops, netbooks), allowing them to use the Internet anywhere there is a cellular connection. It is also suitable for poorly accessible areas and places with poorly developed cable networks. For example, using a mobile connection can be very useful in a suburban area.

Compact 3G modem in the formUSB key fob
The main advantages of this connection method include high mobility and almost universal availability of connections in areas covered by cellular networks. Under favorable conditions, using modern 3G routers, mobile Internet speeds can reach 7 Mbit/s, and support for Wi-Fi technology will allow you to organize a connection to the global network for several devices at once.

But as always, there is a fly in the ointment, which may make it impractical to use this type of connection as the main one at home. The speed of such a connection greatly depends on the mobile operator and becomes acceptable only in 3G networks, the coverage density of which is not yet very high in the Russian Federation. Unfortunately, in many cases (lack of 3G networks, poor signal level), the speed of mobile Internet leaves much to be desired and is slightly superior in its characteristics to dial-up access. And this, in turn, imposes certain restrictions on its functionality.
We also note that with limited tariffs (imposing restrictions on the amount of information received from the Internet), allowing the use of mobile Internet at maximum speeds, the cost of traffic for such a connection will be quite high for many users. In the increasingly popular unlimited tariffs, as a rule, there is a serious limitation on the connection speed, which can be imposed after exceeding the unofficially established limit on the amount of downloaded data from their network.
Required equipment:
- Cable connecting the phone to the computer when using a phone
- GPRS/3G modem or router
SATELLITE INTERNET.
This method makes it possible to permanently connect computers to the network that are located considerable distances away from telephone lines (dacha area), and will also be useful in hard-to-reach areas with poor cellular signal reception.
Satellite connections can be asynchronous (one-way) or synchronous (two-way). We will not consider the second connection method, due to the high cost of the equipment (here the bill runs into tens of thousands of rubles).
Most often, satellite Internet is called an asynchronous (combined) access method - this is when information arrives to the user via a satellite dish, and the request for traffic from the user is transmitted by another connection - for example, through GPRS, ADSL or Dial-Up. It should be noted that the main requirement for the request channel is connection reliability.
The data transfer speed with this connection method can range from 256 to 4000 Kbps and greatly depends not only on the provider, but also on the chosen tariff plan.

The main advantage of a satellite connection to the Internet is the extremely low price of traffic (from 10 kopecks to 1 ruble per 1 megabyte), the ability to organize connections in remote areas, thanks to independence from land lines and the availability of satellite television.
The disadvantages include: the need to have a channel for outgoing traffic - usually a cell phone with GPRS support and the fairly high cost of equipment and its installation.
Required equipment:
- Satellite dish with bracket
- DVB card for decoding satellite signal
- Converter
CONCLUSION
So, having considered all the main ways to connect to the global Internet, let’s summarize. Undoubtedly, the fastest and highest quality connection to the global network will be wired broadband access. Data exchange through peer-to-peer networks, IP telephony, IP television, local resources of local networks, deployment of your own wireless Wi-Fi network and of course full use of all kinds of Internet services - all this will be available to you when using this high-speed connection. Unfortunately, this type of connection is only available in large cities where fiber optic communication lines are installed.
A good alternative to broadband access is ADSL technology, which also allows high-speed network access (up to 8 Mbit/s) and quite efficient use of all the capabilities of the Internet. True, those who like to exchange files using torrent clients may encounter serious troubles due to the peculiarities of this technology, and as a result, the low upload speed. You should also remember that the presence of a telephone line does not yet guarantee that you will be able to use this connection method, since another necessary condition is the placement of special ADSL equipment on your PBX.
The use of mobile technologies to connect to the network at home is most advisable in areas with low cable coverage, as well as in highly inflated tariffs for wired Internet services. But remember that comfortable work on the global network is only possible in third-generation 3G cellular networks. Otherwise, the speed of information exchange will leave much to be desired. And of course, this connection method is most in demand by owners of cell phones, tablets, netbooks and other mobile devices who want to have access to the Internet anywhere in the coverage area of cellular networks.
If you are planning to connect to the Internet in a place with a low level of cable coverage, where there are no fixed telephone lines or local telephone exchanges are not equipped with specialized equipment, and there are no 3G mobile networks, then satellite Internet will be the most optimal solution. Low cost of traffic, acceptable data exchange speed and the ability to watch satellite television are the main advantages of such a connection among wireless solutions. True, you will have to fork out money for the purchase and installation of equipment.
The promising MobileWiMAX technology has the undoubted advantage of high speed and ease of connecting to the network. Essentially, it's the Internet in your pocket. In a matter of minutes, almost any computer can be connected to the World Wide Web using a miniature modem designed in the form of a USB key fob. Only the coverage area of such networks in Russia is now negligible, and the thick walls of your house can become an insurmountable obstacle to the passage of a weak signal. So before choosing this connection method, check out the coverage area in your region and its availability in general.
Connection using dial-up access (Dial-Up) today can be considered completely outdated, and its use can only be imagined as a budget option on telephone lines that do not support ADSL technology.
In conclusion, let's say a few words about prices. In large cities of Russia, due to the growing competition between Internet providers and the massive development of local networks, access to the World Wide Web is becoming less and less expensive. From the point of view of choosing a tariff plan, unlimited Internet access with a fixed monthly subscription fee can be considered the most profitable. For example, in Moscow for 400 - 500 rubles per month you can connect to the network at a speed of 8 - 10 Mbit/s, the cost of unlimited mobile Internet will cost you 390 rubles, and connecting to MobileWiMAX at maximum speed will cost 1,400 rubles. But in provinces or small towns, prices for services providing access to the global network can be greatly inflated due to weak competition among providers or its complete absence. In such cases, pay attention to mobile connection tariffs or satellite Internet, in which pricing does not depend on the region.
That's all. Good luck connecting to the global network!
There are quite a large number of types of connections to the Internet provider. Below are the main ones:
1. Local network connection
In this case, the user connects via a regular Ethernet local network. No additional connections or login/password entry is required. This type is further subdivided into:
a) Dynamic - DHCP or "dynamic". The simplest type, no settings are required and the user simply connects the computer with a cable, which receives all settings automatically
b) Static -"fixed IP address" or "static". In this case, preliminary configuration of the “Internet Protocol TCP/IPv4” parameters is required according to the settings provided by the provider and usually includes the IP address, subnet mask, gateway and DNS server(s). For example, this type is used by the TDS+ provider in Volokolamsk.
Sometimes both subtypes can be used binding by MAC address(in this case, the router is usually required to support the so-called MAC Cloning or MAC Spoofing - substituting or changing the MAC address on an Internet port).
2. VPN connection
In this case, the user connects via the so-called. VPN (virtual private network) with the need to specify a login and password. This type has divisions:
a) PPPoE. To connect to the Internet, you need to create a connection through the setup wizard by selecting “Connect to the Internet” -> “Set up a connection manually” and select PPPoE in the settings.
b) PPTP. To connect to the Internet, you need to create a connection through the setup wizard by selecting “Connect to a workplace” -> “Connect to a virtual private network (VPN)”, then specify the VPN server address.
c) L2TP. Another type of connection that is gaining popularity. The setup is similar to PPTP, only after creating a connection, you need to select “L2TP IPSec VPN” in its properties on the “Network” tab.
You can also find out the type of VPN connection by clicking on the connection icon in the tray (when the Internet is active) and selecting the “Details” tab.
3. Combined connection type
The most complex type, widespread, in fact, only in Russia (with rare exceptions). The bottom line is to combine a local network connection with a VPN connection to provide the so-called. Dual access— double access, i.e. access to the Internet and internal resources of the provider (peer-to-peer networks, IPTV, etc.). Accordingly, various combinations of (1) and (2) can be used, namely:
a) PPPoE + Dynamic. The Internet is provided via PPPoE, the local address in the provider’s network is obtained automatically. Usually, routes are also dynamically distributed for accessing certain resources through a particular interface (using the so-called DHCP option). For example, this type is used by the Chekhov provider Chehov.NET
b) PPPoE + Static. The Internet is provided via PPPoE, the local address in the provider’s network is set manually, statically. Routes are also registered manually using the “route add …” command in the “cmd” console.
c) PPTP + Dynamic. The Internet is provided via PPTP, the local address in the provider’s network is obtained automatically. Routes can similarly be distributed dynamically via the DHCP option or specified manually (rarely).
d) PPTP + Static. The Internet is provided via PPTP, the local address in the provider’s network is set manually, statically. Routes are also written manually.
e) L2TP + Dynamic. The Internet is provided via L2TP, the local address in the provider’s network is obtained automatically. Routes can similarly be distributed dynamically via the DHCP option or specified manually (rarely).
f) L2TP + Static. The Internet is provided via L2TP, the local address in the provider’s network is set manually, statically. Routes are also written manually.
P.S. Determining your type of Internet connection will help you set up your Wi-Fi router or Wi-Fi access point.
The information technology market has literally become overgrown with companies that provide Internet access services. What technologies are not offered today in wireless and wired connections to maximally cover hard-to-reach areas, increase data transfer speeds, and improve communication quality.
As many people know, first of all, different Internet providers differ in the type of services they provide, namely the type of access to the Internet.
An Internet provider is a company that provides Internet access to customers and provides related services.
There are many different types of internet connections. These include broadband, dial-up and wireless communication lines. All of them are capable of providing access to the Internet, although they work on different principles. Let's look at everything in order.
Ethernet – local network connection
This is broadband access to the Internet via a separate line. The line laid by the provider is based on fiber optic or copper cable and allows you to transfer data at very impressive speeds. A fiber optic cable differs from a copper cable in that the main material in it is glass or plastic, and information is transmitted through it not by an electrical signal, but by a light signal. This allows you to broadcast a signal with minimal attenuation and maximum transmission speed.
Leased line
Copper cable most often means twisted pair. Through it, information is transmitted by an electrical signal. Twisted pair, unlike optical fiber, has a significant signal attenuation rate and is susceptible to electromagnetic interference. To increase the length of the communication channel, cables with interference protection should be used, and to reduce the signal attenuation coefficient, special correctors or signal buffers should be used.
Do Internet providers do this in practice? Typically, fiber optic cable is used to connect the subprovider to the backbone provider and connect various buildings (homes, hotels) to the global network, and then there is twisted pair cable.
GPON (gigabit passive optical network) technology is now actively developing. Its essence is that the provider runs a fiber optic cable directly to your apartment and installs a special distribution box. As a result, you technically have the opportunity to connect to the global network at a speed of 1 Gbit/s, but in other cases the speed will not exceed hundreds of Mbit/s.
Modem connection (ADSL/Dial-Up)
Dial-up Internet access via a regular telephone line using a modem. There is both the old Dial-Up technology and the more advanced ADSL. Connecting to a provider via ADSL, unlike Dial-Up, allows you to surf the Internet and simultaneously make phone calls. This is achieved through an ADSL splitter, which separates the telephone signal into a regular telephone signal and a high-frequency modem signal.

Compared to a dedicated line connection, the advantage of a modem connection is the use of already existing infrastructure - telephone cables. This is where the advantages of this type of connection end. The maximum data transfer rate for Dial-Up is 56 Kbps, and for ADSL technology 24 Mbps. Considering the state of most telephone lines, there may not be such indicators about the stability of the connection. As you understand, a telephone line is inferior to a leased line in all respects, taking into account the stable growth of multimedia and the volume of transmitted data. Just a few years ago this type of connection was considered one of the best, but these days it has practically become obsolete despite its still active use.
Internet connection using DOCSIS technology
Literally, DOCSIS is translated as a standard for data transmission over coaxial (TV) cable. Information transmission according to this standard is carried out to the client at a speed of 42/38 Mbit/s, and from the user at 10/9 Mbit/s. It is worth noting that the bandwidth in this technology is divided between all connected participants who are currently receiving or sending a stream. Consequently, the available bandwidth at the time of data transmission or reception for each participant can vary widely.
This method is implemented through a special modem. We are talking about a cable modem for DOCSIS technology with a built-in network bridge, which makes it possible to exchange data over a coaxial or optical cable in two-way mode. In the network of such a provider there is a CMTS device - Cable Modem Termination System. Simply put, this device is a large modem in the backbone network to which subscriber modems are connected.
From an economic point of view, laying a coaxial cable in order to gain access to the Internet is not very reasonable; it is better to install a dedicated line, because such a line has better characteristics, but if you already have a TV cable and the operator provides such a service, then why not? take advantage of. However, if the provider can offer Internet using FTTB, PON or HCNA technologies, then due to a number of technical advantages it is better to choose one of them instead of DOCSIS.
Mobile Internet access (GPRS, EDGE, 3G)
This type of connection is popular because it allows you to access the Internet even where there is no telephone or leased line. You can connect to your Internet provider using a USB 3G modem or using a regular mobile phone that supports the modem function. A USB modem is visually similar to a USB flash drive and has a slot inside for installing a SIM card.

Connecting to the Internet via a USB modem or mobile phone is performed by contacting the base station of the cellular operator with which the SIM card is registered, and depending on what equipment is installed by the mobile provider, communication is established using GPRS, EDGE, 3G or 4G technology. Thus, after connecting a USB modem or phone to a computer, you will have access to the Internet using one of the mentioned technologies.
Mobile Internet has a rather unstable connection and sometimes not high speed, but as they say, it’s better than nothing. The maximum data transfer speed in the presented technologies is on average 30-60 Kbps in GPRS; 100-256 Kbps in EDGE; 144 Kbps - 3.6 Mbps in 3G and 4G can exceed 100 Mbps, and for landline subscribers it can be 1 Gbps.
The speed may in some cases be higher, but in almost all cases it is lower. Mobile Internet, of course, has its drawbacks, but being able to access the Internet from anywhere in the country where there is cellular communication captivates many.
Internet via satellite
To connect even to one-way satellite Internet, you will need a set of special equipment. The minimum input package includes a satellite antenna, a converter amplifier, a satellite receiver, an RG-6 cable of the required length and a pair of F-connectors.
For two-way satellite Internet you need a transceiver antenna (about 1.2 - 1.8 meters in diameter), a transmitting BUC converter and a receiving LNB unit and a satellite modem, to which you can connect not one, but several computers and provide them with Internet access .

Satellite Internet
With two-way Internet access, no additional channels are needed, since data is sent and received via satellite. Many satellite Internet operators can offer both unlimited packages and a pay-per-traffic tariff. Two-way satellite Internet for some operators is faster than 3G technology, and the speed in the Ka-band can be 20 Mbit/s.
The disadvantages of satellite Internet include the high cost of equipment, complexity of setup and decent response time. Typically, this type of communication is used in the most remote corners, where there are no other communication options.
Internet connection using WiMax technology
In addition to other types of Internet connections, you should pay attention to the very interesting WiMax technology. Typically, this technology is used where cable Internet of the DOCSIS standard is not available, there is no dedicated network in the home or office, or there is no telephone line for an ADSL connection. Access to the global network via WiMax technology, as well as via satellite connection, is often an excellent choice in such cases.
WiMax technology is theoretically designed for a speed of about 70 Mbit/s, but in reality it is usually several times less. To connect to the Internet via WiMax, you should contact the appropriate provider, who will determine from the network coverage map whether the desired location is supported by the coverage area. If it turns out that the location is not within the coverage area, then specialists will need to determine the distance to the nearest base station to you.
It is desirable that the base station is in direct visibility from the subscriber, and the distance is no more than 10 kilometers. Depending on the results obtained, you will need to select the desired WiMax modem and antenna with the required gain. In addition, you need a cable to connect the antenna to the modem and a USB extension cable to connect the modem to a computer or switch.